PESTLE factors
Chocolate is often given as a romantic gift because it's believed to have properties that can help set the mood for love. Chocolate has a combination of rich ingredients, including sweet-smelling cocoa butter, energizing caffeine and theobromine and just a touch of stimulant similar to our natural endorphins, which can give you a feeling of well-being and lower your inhibitions. Give your lover some and see how he or she turns dinner into an evening of romance.
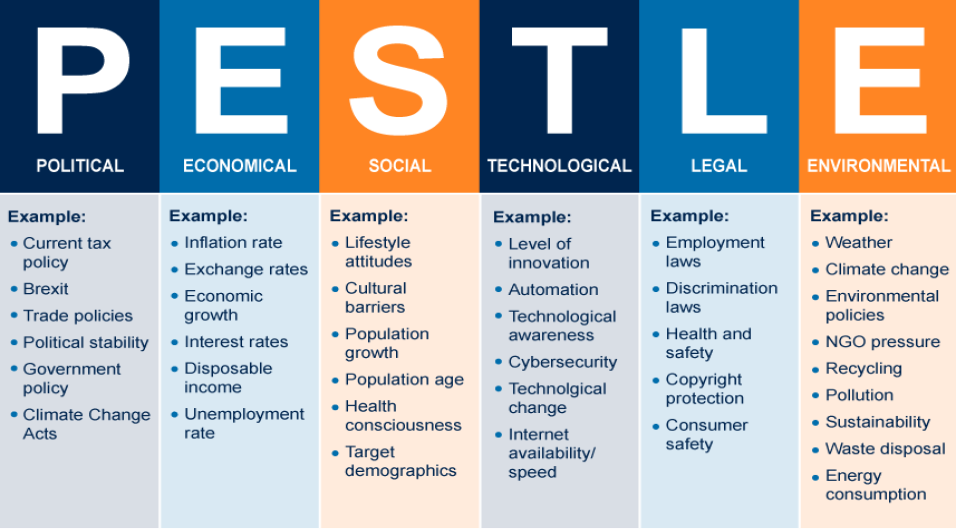
For business organizations to operate effectively, they must have room for carrying out a critical in-depth analysis of the many factors that are likely to influence operations as well as strategic choices. This model is PESTLE, a widely applied analytical tool with the following components: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors. The discussion will critically analyze these PESTLE factors and how each of the elements can impact businesses. This kind of scrutiny helps other different interplaying factors, showing organizations where challenges are and what leverages opportunities there are for making informed decisions about sustainable growth and success.
Political factors
Factors Of A Political Nature
Government stability has a considerable influence on the business environment. For example, tax policies and trade agreements are fundamental to the operation of a business in that their effects impinge directly on the operational modalities of the firm. An example is given whereby instability directly at a country results into uncertainty and disruptions which could be supply chain efforts to production and distribution. Just like another key important other dimension, businesses have to take into consideration the political risk when working across the globe such that anticipation of the possible challenges is done and proper act in light to temper the possible effects. Such will involve opportunities created either externally with regard to new markets or even internally for process optimization by policy changes.
Such factors as Political have not stopped having an impact on business environments; such things as the stability of a government and its policies continue to play very important roles in determining what economic activities will be like. This helps businesses consider the possible impacts that could result from political instability, changes of regimes, or even geopolitical tensions. Indeed, host government decisions, whether they are related to changes in tax policies or to further issues of trade agreements and regulations, can have a significant influence on businesses' opportunities for market expansion and profit-making in any country. Political risk is likely complicated to manage but promptly dealt with upon close monitoring of political developments and active stakeholder relationships that would allow expected changes in regulations for risks to be equally moderated and beneficial opportunities exploited by organizations in rapidly changing political landscapes.
Economic factors
Economic Factors Affecting Businesses
Such factors are seen as pivotal in determining business performance and strategy. Market trends and economic indicators provide quick views concerning GDP growth rates and levels of unemployment regarding the overall economic health of the country or region. Inflation rates and currency exchange fluctuations will affect production costs plus pricing strategies and profitability. Business performance is very dependent on how freely consumer spending behavior allows them to sell their wares and the services sold. The monitoring of economic factors by an organization helps it reposition its productions to attract more buyers and also identify market opportunities.
Economic Factors play the most significant role in influencing business decision-making and market dynamics. They have a bearing on strategic planning, resource allocation, and growth strategies. In any marketing campaign, an insight into prevailing market trends and economic indicators works to turn around consumer behaviour towards demand patterns and insulation of competitive forces within industries, hence appropriate repositioning by firms to meet the ever-changing market environment. The fluctuation in inflation rates and currency values affects pricing strategies besides the dynamics of export and import that have an ultimate influence on profitability levels and competitiveness of an entity. Equally important is the knowledge of changes in consumer spending patterns and income levels, as it allows companies to more appropriately adjust their product portfolio to new market requirements and trends, which improves customer satisfaction and market positioning.
Indeed, the current situation in the EU is a far cry from what it was like a year or so ago. With COVID-19 having turned the world inside out, people were forced to respond to a wide array of new challenges that nobody could have foreseen. From one day to the next, the abrupt closure of schools made things incredibly difficult for working parents, with this sudden and unforeseeable change causing chaos for many families across the EU. The dip in the early-participation rate also reflects big declines in the service sectors, particularly in industries that have been hit hard by the pandemic such as events, cultural and recreational activities, and hospitality. That said, based on the efforts from all Member States during this time, this portion is likely to increase in comparison to when these numbers truly reached their peak. With the economy operating at pre-pandemic levels of production and a properly function labor market, Member States would be able to take a bigger jump in these set goals than they are able to at this moment. Recommended actions remain unaltered at 15 Member States, while they are gradually reducing in the Netherlands. Action does not change in Belgium because they are no longer thought to be taken into effect at any time recently, except at this specific moment now. It is thoroughly enjoyable to see that these twenty Member States have decided to act together and push the integration forward, even if there are splits on the pace this should really happen. But compared with recent years, efforts remain tough with remarkable laying behind performances on too many crucial areas of completing the (EMU).
Social Factors
Social Factors include the following: the very broad influences that operate in consumer preferences, market trends, and business behavior. Changes in population characteristics, such as an increase in the proportion of older people in the population or increasing urbanization, may create new markets or change the demand for various products and services. These norms and values have a considerable impact on consumer behavior, as well as on strategies of marketing. The pressure regarding social responsibility and ethical concerns is mounting these days, meaning that businesses need to be aimed at ensuring practices and operations that are sustainable and are within those belonging to communities. Such organizations can relate to customers better and enhance their brand image by recognizing and catering for these social factors.
Besides, Social Factors very significantly influence market patterns, consumer responses, and corporate cultures which, in turn, inform strategies and brand reputation. For instance, prevalence shifting demographic features-such as alterations in ages in a populace or urban-rural can open real ways for firms to tailor their products to specific markets and come up with special lines or services. For example, some cultural norms and values influence the choice of consumers and the kinds of marketing messages followed by those working in the branding field. It is, therefore, important for businesses to attune their strategies to the expectations embedded in society and be accommodative of diversity. For example, taking on social responsibility in business practices lends to developing trust, loyalty, and favorable relations with customers, employees, and communities for long-term sustainability or a good corporate image.
Technological factors
Technological factors are another of the key external environmental factors that can have a large effect on businesses and organizations
Factors such as technology have been integral in the achievement of business success and facilitating innovation in this Informational era. The fast-evolving technologies and innovations like Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain are disrupting sectors of the economy and redefining competitiveness. The resultant effects of automation and digitalization on business operations, replacing creation procedures to customer relations, further makes the case for companies to adopt digital technologies if they are to stay competitive. On the flip side, as much as there are benefits because of technological advancements, for instance in data security, it could be a source of question primarily on the same issue as privacy for companies that should need to employ tough measures implemented within their businesses and follow regulatory protocols to protect and feed on customer trust.
The Technological Factors drive innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness through reshaping business models and customer experiences. They also open new opportunities for evolving operational processes within the market through applying the latest advances in IT to increase productivity. The acceleration that automation and digitalization bring to traditional processes, including manufacturing and customer support, reiterates the need to embrace digital technologies if one is to remain agile and pertinent in fast-paced markets. On the other hand, the increasing number of technological advancements heightens the problem of data security concerning privacy. It calls for companies to engage in compliant robust cybersecurity measures and ethical data practices as a guarantee of keeping close consumer trust in fully digitalized worlds.
Legal Factors
Legal Factors have to be complied with by businesses operating within them form the regulatory framework within which businesses operate and must comply. It could therefore be safely stated that businesses could operate in environments that were more relaxed, thereby being free to make more independent choices without encountering too much interference from governmental control. Other intellectual property rights (IPRs), including patents and trademarks, have given firms a huge advantage in protecting innovation across all industries. Firms from all industries are also safeguarded by many employment laws and workplace regulations that are available under the rights of employees, working conditions, and labour practices. Businesses must meet these standards to ensure that their workforce is treated fairly and ethically. In other words, the organizations are required to comply with the legislation that is in force in a given country, which we can maintain as they are supposed to be clean at any given time of operation.
Legal Factors, therefore, serve to shape the operational landscape for businesses by offering the necessary framework for the conduct of business activities following the law and ethically. Regulatory compliance can help in ensuring that businesses are being operated in adherence to laws and standards which are specific to the industry and are meant for the interest of a consumer so as to keep the market integrity. Innovations and creative works are given protection through Intellectual Property Rights that further enable business organizations to commercialize their offerings in the market while fostering differentiation. Moreover, such respects as employment laws and workplace regulations play directly on the practices related to labour, the rights of employees, and workplace safety to ensure that workers are treated with a level of fairness and ethics, thereby promoting a suitable work environment and organizational culture.
Environmental Factors
Operating and business strategies are now more shaped by the environmental matters that are a response to the global challenges of sustainability. Climate changes bring a number of risks to businesses in many sectors like agriculture, tourism, energy, and hence the organizations have to take responsibility to minimize the impacts on the environment. The laws and regulations on environmental matters introduced by governments are aimed at encouraging environmentally friendly policies, reducing carbon footprints, and making sure that companies are corporately responsible in matters concerning environmental preservation. The other reason why firms should go green by incorporating their corporate social responsibility in their business model is the tie it goes in minimizing cases of environmental degradation since it will boost its branding thereby increasing customer loyalty due to a show of interest in sustainable practices.
Environmental Factors now are pivotal in consideration for those businesses that want to be sustainable in their operations and lessen the impact that emanates from their commercial activities. Business sustainability is a critical phenomenon directly related to the operations of the business and likely to affect organizations’ performance. More and more, climate risks come into sharp focus for businesses across sectors as sustainability initiatives bring down carbon footprints and environmental damage. Governments' environmental regulations and policies center around encouraging eco-initiatives, decreasing the amount of waste produced, and making businesses accountable for their environmental efforts. By implementing the green, eco-initiatives and infusing those into corporate social responsibility companies can enrich their brands’ images. They could also draw environmentally aware clients and essentially take part in conservation activities.
PESTLE-conclusion
PESTLE factors, when taken together, give businesses a much broader frame of the very troubled environment where they have to operate. The very scope of the factor on political aspects spanning government stability, policies, and risk assessments affects the operations of business and market dynamics. Inflation rates plus market trends and even that of consumer behavior form strategic choices because of economic factors. Social factors come in the form of demographic shifts plus cultural norms around technological featured product lines affecting customer preferences. Rapid transformation follows rapid technological advancements and concerns to keep in view data security; thus, digitalization has to charge on protection of privacy. Conformance to legal formalism, eco-centric modes of operations, and the initiation of a corporate social responsibility drive all calls for duly emulated compliance, innovation, and stakeholder engagement. By knowing and reacting to a matrix linked to these issues, firms can happen to change their businesses to capitalize from such opportunities and fire-fight against risks toward overall sustainable development with an edge in the marketplace impacting society at large on a global front.







